Introduction
Heating systems are evaluated by comparing benefit and expenditure as it is done in other technical systems. The benefit of a heating system is to maintain comfortable thermal conditions in the rooms for the occupants. The requirements of the occupants for their thermal environment are independent from the heating system. Usually they specify their demands with nominal temperatures for the room air and for the inside surface temperatures of the walls. These temperatures depend on activity and clothing. A further task of a heating system is to warm up the incoming air from outside, which is necessary because of comfort, health, hygiene and building physics. The delivery of the benefit by the heating system is performed by the so called room system. The planning tasks for a good room system consist of suitable selection, dimensioning and arrangement of the room heating systems.

|
   |
|
It is possible to determine the heat load which must be transfered to a room in order to supply exactly the existing demand, this is the heating load. The time dependent integral over the heating loads – the ideal minimal energy demand Q0 – is an energetic value to compare subsequent processes which satisfy the demands (room system, heat distribution, heat generation). Several national and international norms (DIN EN 832 , DIN 4108-6 or VDI 2067-11) describe how to calculate the building-specific load requirements of heated and air-conditioned buildings.
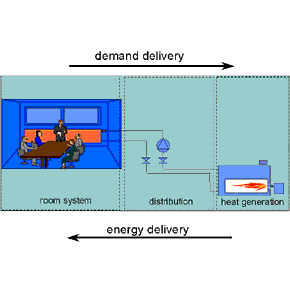
Figure 1 shows the direction of the demand development in a building. Starting from the building itself, its planned usage and the climatic influences the first level is the room system, second level is heat distribution and the third level is the heat generation system. Since each of these subsections cannot be implemented in a perfect way, an additional energy demand, Q1 is caused. If this additional energy demand is brought into relation with the ideal minimized energy demand Q0 , (which is typical for a building and its use), an energy efficiency factor ei can be defined. This will be used as an energetic evaluation value for the individual subsections. Therefore the minimal energy demand Q0 multiplied with the energy efficiency factor ei of each subsection gives the total yearly primary energy demand it is needed by the heat generation system.
|